23
conventional vs telecentric lenses
f-mount
s-mount
c-mount
F-Mount lenses feature a three lug bayonet
mount with a 44 mm throat and a flange to
focal plane distance of 46.5 mm. Mainly used
for high resolution cameras.
S-Mount lenses feature male M12 thread
with 0.5 mm pitch on the lens and a
corresponding female one the lens mount.
Most commonly used with “remote-head”
cameras or with very compact devices like
Vision Sensors.
C-mount lenses provide a male thread
which mates with a female thread on the
camera. Most common standard, used with
VGA resolution (640x480) up to 2 Megapixel
cameras.
Conventional Lenses view in a conical shape and generally produce
magnification errors in radial bands about its center, thus producing
magnification errors when viewing objects at different distances.
Telecentric Lenses offer constant magnification with change in
distance. These lenses are used for high-precision measurement of
objects at different depths.
lens selection
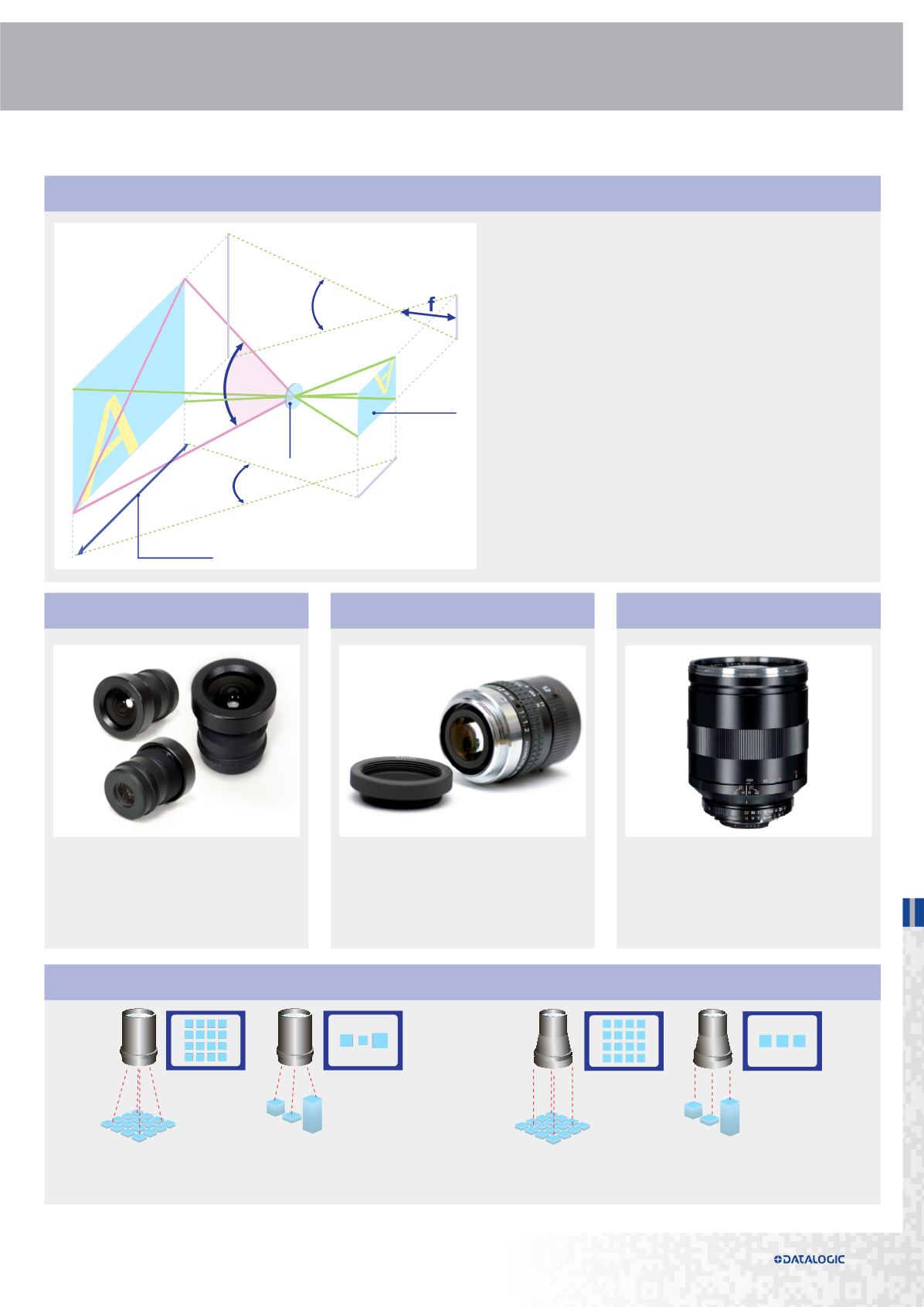
Focal Length:
The focal length of a lens is defined as the distance from the optical
center of the converging lens to the focal point, which is located on
the imager, when “in focus”. Units are typically in mm.
Aperture (f-stop):
The ratio of the focal length of the lens to its effective diameter.
Shown as f-stop or f/f. Each f-stop would allow either 1/2x or 2x
light compare to the next f-stop. A larger aperture opening results in
a smaller f-stop value. Note that the more closed a lens’ aperture is,
the greater the depth of field.
Camera
lens
Field
of view
Vertical
angle
of view
Picture
angle
Horizontal
angle
of view
Camera
sensor
Focal
lenght


